
SIEMENS SAS Training
Module I: Substation Automation System Module II: Bay Level Engineering (IEC 61850 and Modbus) Module III: Station Level Engineering SICAM PAS Module IV: SICAM SCC
SIEMENS SAS Training Read More »

Module I: Substation Automation System Module II: Bay Level Engineering (IEC 61850 and Modbus) Module III: Station Level Engineering SICAM PAS Module IV: SICAM SCC
SIEMENS SAS Training Read More »

(Created: Dec 2018) (Last update: Sep 2023) In this course, you will learn how to use and configure the IEC 61850 station IEC 61850 Configuration Video Training Main Course Updates and Supplementary Files Helpful Files: IEC protocols for substation communications IEC 61850 Technical Overview Download the IEC 61850 training package Details Course Part 1: Substation
IEC 61850 Training Read More »
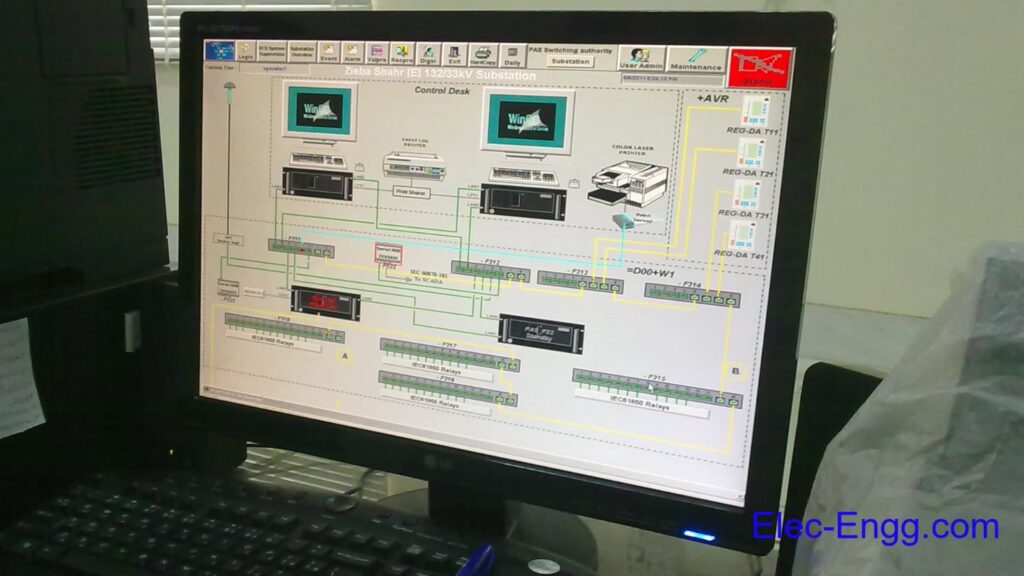
Substation Automation System Hardware Bay Level Engineering (IEC 61850 and Modbus) Station Level Engineering SICAM PAS SICAM PAS UI-Operation SICAM PAS Value Viewer SICAM PQS SCADA SICAM SCC Redundancy Example: Switching Authority in SICAM PAS OPC Communication Additional Information Hardware Setup for SIEMENS SAS training
SIEMENS Substation Automation System Read More »

Topics: Substation Automation System: Network & Ethernet: IEC 61850: SIEMENS SAS Practical Section working with SIPROTEC 5 multifunction relay IED 7SX800 SICAM PAS stands for “Substation Automation System Process Automation Station,” which is a comprehensive solution for monitoring, controlling, and automating various processes in substations. It is designed to improve the efficiency, reliability, and safety
Training on Substation Automation System using IEC 61850 Read More »
IP communication is being extensively introduced into the operation of the Electrical Power Utility. The substation IP network environment has evolved from acting as an extension of the office LAN to a state, where it is carrying multiple services, including the transport of critical and sensitive data.IP communication, being a one-platform solution that relieves you
Communication Architecture for IP-Based Substation Applications Read More »

(Created: . .) (Last update: . .) This course is an overview of the application, properties, and functional scope of the 6MD bay controller. Also, the configuration and parameters of the 6MD IED are presented in this training.
SIPROTEC 6MD Bay Controller training Read More »

20 WhatsApp Groups for protection engineers to join: WhatsApp Grp 01: Protection Relay – General WhatsApp Grp 02: Substation Automation – General WhatsApp Grp 03: Transmission line protection WhatsApp Grp 04: Transformer protection WhatsApp Grp 05: Motor protection WhatsApp Grp 06: Generator protection WhatsApp Grp 07: Overcurrent and Earth Fault Protection WhatsApp Grp 08: Busbar
20 WhatsApp Groups for protection engineers Read More »

contact us to get this impressive IEC61850 collection
IEC 61850 collection Read More »